Ultraviolet visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometers use a light source to illuminate a sample with light across the UV to the visible wavelength range (typically 190 to 900 nm). The instruments then measure the light absorbed, transmitted, or reflected by the sample at each wavelength.
What is UV Vis spectra?
UV-Vis Spectroscopy (or Spectrophotometry) is a quantitative technique used to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light. This is done by measuring the intensity of light that passes through a sample with respect to the intensity of light through a reference sample or blank.
What is the UV Vis spectrum?
UV-vis spectroscopy is a cost-effective, simple, versatile, non-destructive, analytical technique suitable for a large spectrum of organic compounds and some inorganic species. As a function of wavelength, UV-vis spectrophotometers measure the absorption or transmission of light that passes through a medium. In order to classify and measure the ...
What are some uses of UV/Vis spectroscopy?
13.21.1.1: Some Uses of UV/Vis Spectroscopy
- Electronic transitions. Let's take as our first example the simple case of molecular hydrogen, H 2. ...
- Looking at UV-vis spectra. We have been talking in general terms about how molecules absorb UV and visible light - now let's look at some actual examples of data from ...
- Applications of UV spectroscopy in organic and biological chemistry
How does UV Vis spectroscopy work?
How does UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy work? A UV-Vis spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light transmitted through a sample compared to a reference measurement of the incident light source. The transmitted light is acquired by a CCD optical detector with a wavelength accuracy of within 0.5nm.
What is UV-VIS spectroscopy?
What is UV-VIS data?
What is the difference between a single beam and a double beam spectrometer?
Does UV spectroscopy work on liquids?
See 1 more
About this website
How does UV Spectrophotometer measure absorbance?
With UV-Vis spectroscopy, the UV-Vis light is passed through a sample and the transmittance of light by a sample is measured. From the transmittance (T), the absorbance can be calculated as A=-log (T). An absorbance spectrum is obtained that shows the absorbance of a compound at different wavelengths.
How a Spectrophotometer works step by step?
3:585:04How do you use a Spectrophotometer? A step-by-step ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNote that the cuvette is designed for light waves to pass through it in a specific. Direction makeMoreNote that the cuvette is designed for light waves to pass through it in a specific. Direction make sure you orient it in the spectrophotometer. So that the light beam goes through it the right.
How does a spectrometer work?
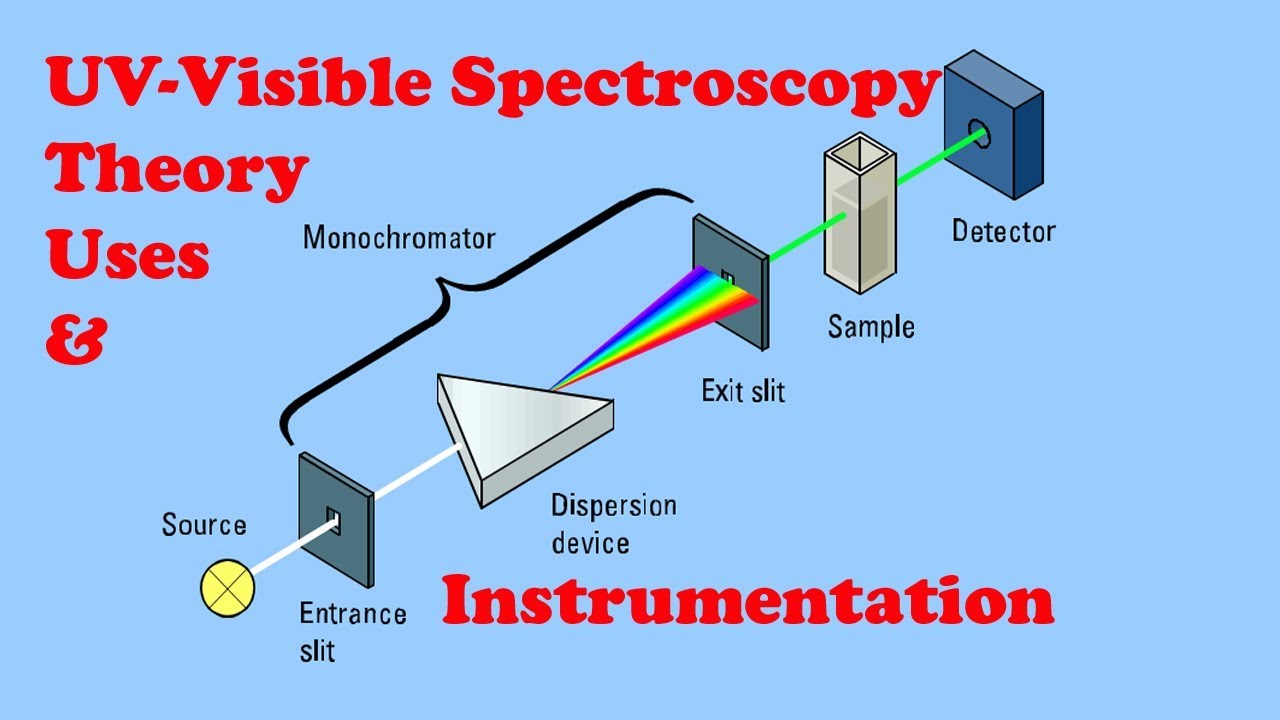
The beam of light strikes the diffraction grating, which works like a prism and separates the light into its component wavelengths. The grating is rotated so that only a specific wavelength of light reaches the exit slit. Then the light interacts with the sample.
What does UV-Vis spectroscopy detect?
UV/Vis spectroscopy is routinely used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of diverse analytes or sample, such as transition metal ions, highly conjugated organic compounds, and biological macromolecules.
How does spectrophotometer measure color?
Spectrophotometers measure reflected or transmitted light across the spectrum and create a visual curve that describes the color on that substrate, under that lighting condition.
How does spectrophotometer work and the principles behind it?
The spectrophotometer works by passing a light beam through a sample to measure the light intensity of a sample. These instruments are used in the process of measuring colour and used for monitoring colour accuracy throughout production. They are primarily used by researchers and manufacturers everywhere.
How does a spectrometer measure wavelength?
How does a Spectrophotometer work? Spectrophotometry is a standard and inexpensive technique to measure light absorption or the amount of chemicals in a solution. It uses a light beam which passes through the sample, and each compound in the solution absorbs or transmits light over a certain wavelength.
How can a spectrometer be used to measure wavelength?
Plug in and turn on the spectrophotometer. Allow it to warm up for 15 minutes. Press the Percent T/A selector to select Percent Transmittance or Percent Absorbance mode. Locate the wavelength dial beside the sample chamber and set it to the desired wavelength.
What does a spectrometer detect?
A spectrometer measures the wavelength and frequency of light, and allows us to identify and analyse the atoms in a sample we place within it.
Why molecules absorb in UV visible region?
Ultraviolet-visible absorption is a process where a molecule absorbs ultraviolet or visible light that excites electrons (makes them high energy). This energy causes an electronic transition from a ground state (non excited) to an excited state.
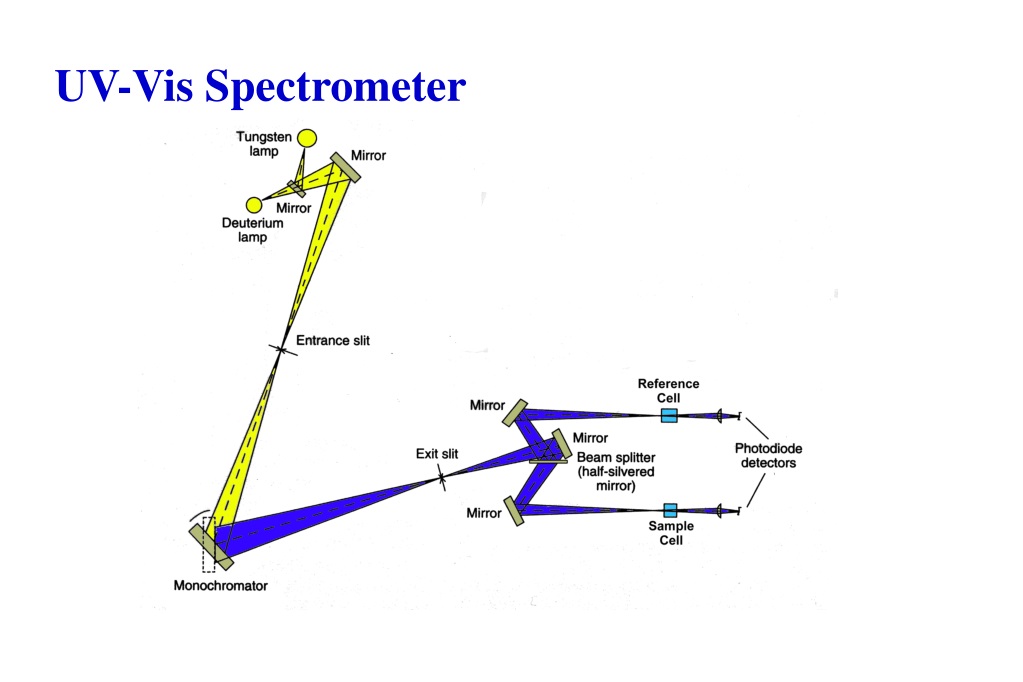
What are the main components of a UV-Vis spectrophotometer?
UV–visible spectrophotometers have five main components: the light source, monochromator, sample holder, detector, and interpreter.
Which transitions are studied by UV spectrometer?
Ultra Violet Spectrometer is basically used to study electronic transitions. It is mainly used for the measurement of reflectance of transparent solids and solutions as well as the intensity of a light beam.
What are the 6 parts of a spectrophotometer?
Spectrophotometer: Meaning, Parts and Operation | BiotechnologyBeer Lambert's Law: ... There are six parts in a spectrophotometer: ... Light Sources: ... Monochromators: ... Cuvettes: ... Photocell or photomultiplier tube: ... λ max of proteins: ... X Max of Nucleic Acids.More items...
How does a spectrophotometer work quizlet?
When light passes through a filter or prism it gets broken into its component wavelengths. When light passes through a filter, some wavelengths get absorbed (taken in) and other transmitted (pass through).
What is spectrophotometric method?
Spectrophotometry is an experimental technique that is used to measure the concentration of solutes in a specific solution by calculating the amount of light absorbed by those solutes. [1] This technique is powerful because certain compounds will absorb different wavelengths of light at different intensities.
What are the three main components of a spectrophotometer?
A spectrophotometer consists of three primary components: a light source, optics to deliver and collect the light, and a detector.
The Basics of UV-Vis Spectroscopy - Agilent Technologies
3 1.1 The electromagnetic spectrum Ultraviolet (UV) and visible radiation are a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes other forms of radiation such as radio, infrared
Principle of UV-Visible Spectroscopy - Detailed Explanation - BYJUS
UV-Visible Spectroscopy and the Beer-Lambert Law. The statement of the Beer-Lambert law can be written as follows: When a beam of monochromatic light is made incident on a solution that contains a substance that absorbs the monochromatic light, the rate at which the intensity of the beam decreases along the thickness of the solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the ...
UV VIS Spectroscopy - Definition, Theory & Applications with Videos - BYJUS
UV VIS Spectroscopy - The most commonly used instrumental techniques in analytical chemistry , particularly in the life sciences, are possibly UV-visible spectroscopy. In analytical chemistry, UV-VIS spectroscopy is routinely used for the quantitative determination of various solution analytes. Visit BYJU’S to learn more about it.
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy - Wikipedia
UV spectroscopy or UV–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.Being relatively inexpensive and easily implemented, this methodology is widely used in diverse applied and fundamental applications.
What is UV-VIS spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy is used to obtain the absorbance spectra of a compound in solution or as a solid. What is actually being observed spectroscopically is the absorbance of light energy or electromagnetic radiation, which excites electrons from the ground state to the first singlet excited state of the compound or material. The UV-vis region of energy for the electromagnetic spectrum covers 1.5 - 6.2 eV which relates to a wavelength range of 800 - 200 nm. The Beer-Lambert Law, Equation 4.4.1 , is the principle behind absorbance spectroscopy. For a single wavelength, A is absorbance (unitless, usually seen as arb. units or arbitrary units), ε is the molar absorptivity of the compound or molecule in solution (M -1 cm -1 ), b is the path length of the cuvette or sample holder (usually 1 cm), and c is the concentration of the solution (M).
What is UV-VIS data?
UV-vis spectroscopic data can give qualitative and quantitative information of a given compound or molecule. Irrespective of whether quantitative or qualitative information is required it is important to use a reference cell to zero the instrument for the solvent the compound is in. For quantitative information on the compound, calibrating the instrument using known concentrations of the compound in question in a solution with the same solvent as the unknown sample would be required. If the information needed is just proof that a compound is in the sample being analyzed, a calibration curve will not be necessary; however, if a degradation study or reaction is being performed, and concentration of the compound in solution is required, thus a calibration curve is needed.
What is the difference between a single beam and a double beam spectrometer?
1) has a filter or a monochromator between the source and the sample to analyze one wavelength at a time. The double beam instrument (Figure 4.4. 2) has a single source and a monochromator and then there is a splitter and a series of mirrors to get the beam to a reference sample and the sample to be analyzed , this allows for more accurate readings. In contrast, the simultaneous instrument (Figure 4.4. 3) does not have a monochromator between the sample and the source; instead, it has a diode array detector that allows the instrument to simultaneously detect the absorbance at all wavelengths. The simultaneous instrument is usually much faster and more efficient, but all of these types of spectrometers work well.
Does UV spectroscopy work on liquids?
UV-vis spectroscopy works well on liquids and solutions, but if the sample is more of a suspension of solid particles in liquid, the sample will scatter the light more than absorb the light and the data will be very skewed. Most UV-vis instruments can analyze solid samples or suspensions with a diffraction apparatus (Figure 4.4. 7 ), but this is not common. UV-vis instruments generally analyze liquids and solutions most efficiently.
What is UV spectroscopy?
UV Vis spectroscopy is a type of absorption spectroscopy in which a sample is illuminated with electromagnetic rays of various wavelengths in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible (Vis) ranges. Depending on the substance, the UV or visible light rays are partially absorbed by the sample. The remaining light, i.e. the transmitted light, is recorded as a function of wavelength by a suitable detector. The detector then produces the sample's unique UV Vis spectrum (also known as the absorption spectrum).
Why is the sample compartment open in UV spectrophotometers?
The sample compartment in UV Vis array spectrophotometers is open due to the fact that array instruments use reverse optics and the simultaneous detection of all wavelengths of the spectrum.
How to measure transmittance in a spectrophotometer?
In a spectrophotometer the transmittance is measured by dividing the intensity spectrum of light transmitted through a sample (I) by the intensity spectrum of light transmitted through the blank (I 0 ).
How to analyze a compound with UV spectroscopy?
Molecules can be analyzed using UV Vis spectroscopy if they possess any functional group or conjugation, or if they produce a color complex. As inorganic compounds do not contain any functional group or conjugation, the common method for analyzing them is by reaction with a suitable compound. This produces a color complex whose absorbance can be photometrically measured in the visible region and correlated with its actual concentration. For example, iron is commonly analyzed by a reaction with 1, 10-phenthroline to produce a red color complex. The absorbance of the complex is measured at 570 nm to estimate iron concentration.
What are the different types of spectroscopic techniques?
The spectroscopic techniques commonly used for chemical analysis are atomic spectroscopy, ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy (UV Vis spectroscopy), infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance .
What happens when light hits an object?
When light hits an object, it can be absorbed by the object , typically because the wavelength of the absorbed light corresponds to an electronic excitation in the object. The remaining light is transmitted, i.e. it passes through the object.
What happens to the absorption of UV light?
The absorption of UV light results in electronic transitions from lower energy levels to higher energy levels. Absorption of ultraviolet radiation in organic molecules is restricted to certain functional groups (chromophores) that contain valence electrons of low excitation energy. The molecular transitions/interactions that take place due to UV absorption are:
What is UV VIS Spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
What is UV Vis?
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV / Vis) in the ultraviolet-visible spectral field refers to absorption spectroscopy ...
What is UV spectrophotometer?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, about the levels of active ingredients present in pharmaceutical compounds.
What wavelength is used to determine the concentration of an analyte?
In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a solution in a cuvette with a wavelength ranging between 180 and 1100 nm. The sample absorbs this UV or visible radiation in the cuvette.
What is the wavelength of UV spectroscopy?
The UV frequency is between 100 and 400 nm, and the visible spectrum is between 400 and 700 nm.
What is the principle of IR spectroscopy?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corresponding structure. The energies depend on the form of the molecular surfaces, the vibronic coupling associated with them and the mass corresponding to the atoms.
Where are UV visible spectrophotometers used?
UV-Visible Mid-range to Upper-end Spectrophotometers are typically used in research laboratories, including university and industrial laboratories.
What is UV visible spectroscopy?
UV-Visible spectroscopy exposes the sample to ultraviolet light, which excites the electrons upon absorbance of the light energy. The absorbance is measured based on how excited the electrons become. This type of spectroscopy is commonly used to research the chemical bonding of molecules in the sample material.
How does a Raman spectrometer work?
Raman spectrometers are most often used in chemistry to provide the structural fingerprint to identify molecules. This type of spectroscopy relies on inelastic scattering of photons. It uses a source of monochromatic light, typically from a laser. Generally, it’s in the visible light, near-infrared, or near-ultraviolet spectrum, though it’s also possible to use x-rays. The laser interacts with excitations within the sample, which shifts the energy either up or down. That shift provides information about the vibrational modes, similar to the information infrared spectroscopy offers.
What Does a Spectrophotometer Measure?
Spectrophotometers employ spectrophotometry to measure the transmittance and absorbance properties of any given material as a function of wavelength , thus determining he concentration of an analyte.
What is near IR spectroscopy?
Near IR spectroscopy is based on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation at wavelengths from 780 to 2,400 nanometers. The light interacts with the sample and then the detector measures the transmittance and absorbance. Near IR spectroscopy has a wide range of applications, including, neonatal research, blood sugar, functional neuroimaging, urology, ergonomics, atmospheric chemistry, and more.
What is the photodetector made of?
Photodetector: Light that passes the sample being analyzed hits the photodetector, which is made of semiconducting material. Electrons in the material are excited proportionally to the wavelength that strikes the photodetector. Increasing the light intensity produces additional electrons, so the signal processor receives a higher current.
What is the prism in a spectral microscope?
Prism: Also known as the diffraction grating, this is what separates the light source into specific parts of the spectrum. When the variable wavelength selector is adjusted, the prism’s position changes so that different wavelengths of light are directed toward the sample compartment that contains the object or sample being analyzed.
What is a variable wavelength selector?
Variable wavelength selector: This component is on the outside of the instrument and allows the light to be filtered so that it only transmits light at a certain wavelength or range of wavelengths.
What is UV-VIS spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy is used to obtain the absorbance spectra of a compound in solution or as a solid. What is actually being observed spectroscopically is the absorbance of light energy or electromagnetic radiation, which excites electrons from the ground state to the first singlet excited state of the compound or material. The UV-vis region of energy for the electromagnetic spectrum covers 1.5 - 6.2 eV which relates to a wavelength range of 800 - 200 nm. The Beer-Lambert Law, Equation 4.4.1 , is the principle behind absorbance spectroscopy. For a single wavelength, A is absorbance (unitless, usually seen as arb. units or arbitrary units), ε is the molar absorptivity of the compound or molecule in solution (M -1 cm -1 ), b is the path length of the cuvette or sample holder (usually 1 cm), and c is the concentration of the solution (M).
What is UV-VIS data?
UV-vis spectroscopic data can give qualitative and quantitative information of a given compound or molecule. Irrespective of whether quantitative or qualitative information is required it is important to use a reference cell to zero the instrument for the solvent the compound is in. For quantitative information on the compound, calibrating the instrument using known concentrations of the compound in question in a solution with the same solvent as the unknown sample would be required. If the information needed is just proof that a compound is in the sample being analyzed, a calibration curve will not be necessary; however, if a degradation study or reaction is being performed, and concentration of the compound in solution is required, thus a calibration curve is needed.
What is the difference between a single beam and a double beam spectrometer?
1) has a filter or a monochromator between the source and the sample to analyze one wavelength at a time. The double beam instrument (Figure 4.4. 2) has a single source and a monochromator and then there is a splitter and a series of mirrors to get the beam to a reference sample and the sample to be analyzed , this allows for more accurate readings. In contrast, the simultaneous instrument (Figure 4.4. 3) does not have a monochromator between the sample and the source; instead, it has a diode array detector that allows the instrument to simultaneously detect the absorbance at all wavelengths. The simultaneous instrument is usually much faster and more efficient, but all of these types of spectrometers work well.
Does UV spectroscopy work on liquids?
UV-vis spectroscopy works well on liquids and solutions, but if the sample is more of a suspension of solid particles in liquid, the sample will scatter the light more than absorb the light and the data will be very skewed. Most UV-vis instruments can analyze solid samples or suspensions with a diffraction apparatus (Figure 4.4. 7 ), but this is not common. UV-vis instruments generally analyze liquids and solutions most efficiently.
How Does Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Work?
- To give you a better understanding of how Uv-Vis spectroscopy works, let’s talk about its main components and the processes of how light is absorbed and measured by the spectrometer.
The Purpose and Applications of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy has been widely used in various sample testing today. This technique has the following famous innovative applications:
Advantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The best advantage of utilizing Uv-Vis spectrometers is their optimal accuracy. These machines are guaranteed to give you accurate readings, which are essential when you need to prepare chemical solutions or record the movement of the celestial bodies. Uv-Vis spectroscopy is also easy to understand with its simple analysis ability. The spectrometers are convenient and easy t…
Disadvantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The main disadvantage of Uv-Vis spectrometers is their challenging assembly, and it may take time to prepare using them. Ensure that the area where you’ll place the device is clear of any electronic noise, outside light, and other contaminants that could affect the measurements and readings of the spectrometer. A Uv-Vis spectrometer is sensitive to external factors, so you mus…
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Limitations
- Even an advanced technique like Uv-Vis spectroscopy has limitations, too. You can grasp what these are below:
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Is The Future
- UV-vis spectroscopy provides researchers and scientists with more efficient methods to measure light wavelengths, providing accurate readings that are helpful in various biological and chemical analyses. The UV-vis spectrometer device is precise and easy to operate, provided that you maintain a clean working area free from any external noise and dust that can affect the machine’…