
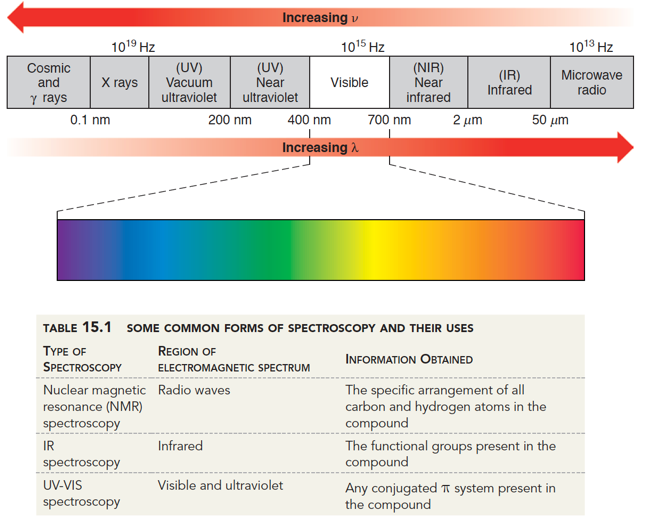
Ultraviolet visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometers use a light source to illuminate a sample with light across the UV to the visible wavelength range (typically 190 to 900 nm). The instruments then measure the light absorbed, transmitted, or reflected by the sample at each wavelength.
What are some uses of UV/Vis spectroscopy?
13.21.1.1: Some Uses of UV/Vis Spectroscopy
- Electronic transitions. Let's take as our first example the simple case of molecular hydrogen, H 2. ...
- Looking at UV-vis spectra. We have been talking in general terms about how molecules absorb UV and visible light - now let's look at some actual examples of data from ...
- Applications of UV spectroscopy in organic and biological chemistry
What is woodwardfieser rule in UV spectroscopy?
These sets of rules to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption or λmax of a compound in the ultraviolet-visible spectrum, based empirically have been called the Woodward-Fieser rules or Woodward’s-rules.
How does UV affect the skin?
UV exposure causes the uneven thickening and thinning of the skin called solar elastosis, resulting in coarse wrinkling and a yellow discoloration. It can also cause the walls of blood vessels to become thinner, leading to easy bruising and spider veining (telangiectasias) on the face.
What are the applications of UV-visible spectroscopy?
Applications of UV-Vis spectroscopy
- DNA and RNA analysis. Rapidly determining the purity and amount of DNA and RNA is one of the most popular applications. ...
- Pharmaceutical analysis. The most popular applications of UV-Vis spectroscopy can be found within the pharmaceutical industry.
- Bacterial culture. ...
- Beverage analysis. ...
- Other applications. ...
How does UV-Vis process data?
0:038:04UV-Vis Tutorial | Part 3: Data Analysis - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIf on the UV vis you measured the peak absorbance at 1 you would multiply that by 100 which givesMoreIf on the UV vis you measured the peak absorbance at 1 you would multiply that by 100 which gives you a dilution corrected Peak absorbance value of 100.
How can UV-Vis spectroscopy be used to determine the concentration of a substance?
This article more specifically explores techniques when using a spectrophotometer to determine concentration of an analyte. A UV/VIS spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light passing through a sample solution in a cuvette, and compares it to the intensity of the light before it passes through the sample.
What does UV-Vis data tell you?
UV-VIS spectrophotometry is a method for measuring the wavelength and intensity of ultraviolet and visible light absorbed by a sample.
What is UV-Vis spectroscopy and how is it used in forensic science?
Abstract. The use of UV/visible spectroscopy has been recommended for forensic applications. UV/visible spectroscopy plays a key role in examining inks and fibers. The UV/visible spectrum directly quantifies the color of the sample and the technique is reliable and simple to carry out experimentally.
Why is UV-Vis spectroscopy important?
UV-VIS spectroscopy, like FTIR, is a technique which is useful in the identification of pure drug compounds. Many molecules contain chromophores which will absorb specific wavelengths of ultra violet or visible light.
How spectrophotometer detect the impurities?
UV absorption spectroscopy is one of the best methods for determination of impurities in organic molecules. Additional peaks can be observed due to impurities in the sample and it can be compared with that of standard raw material. By also measuring the absorbance at specific wavelength, the impurities can be detected.
Is UV spectroscopy quantitative or qualitative?
UV spectrophotometry is an analytical technique used routinely for qualitative and quantitative assay due the low cost and reliability during analysis.
Why molecules absorb in UV visible region?
Ultraviolet-visible absorption is a process where a molecule absorbs ultraviolet or visible light that excites electrons (makes them high energy). This energy causes an electronic transition from a ground state (non excited) to an excited state.
Why quartz cuvette is used in UV?
Quartz cells provide more durability than plastic or glass. Quartz excels at transmitting UV light, and can be used for wavelengths ranging from 190 to 2500 nm.
What is the difference between UV and visible spectroscopy?
There is no difference between UV and visible spectrophotometer because both names refer to the same analytical instrument.
How do you find concentration from absorbance?
In order to derive the concentration of a sample from its absorbance, additional information is required....Absorbance Measurements – the Quick Way to Determine Sample ConcentrationTransmission or transmittance (T) = I/I0 ... Absorbance (A) = log (I0/I) ... Absorbance (A) = C x L x Ɛ => Concentration (C) = A/(L x Ɛ)
How do you determine concentration?
Divide the mass of the solute by the total volume of the solution. Write out the equation C = m/V, where m is the mass of the solute and V is the total volume of the solution. Plug in the values you found for the mass and volume, and divide them to find the concentration of your solution.
What is the relationship between concentration and absorbance?
Introduction: According to Beer's Law, A=Ebc, under ideal conditions, a substance's concentration and its absorbance are directly proportional: a high-concentration solution absorbs more light, and solution of lower concentration absorbs less light.
How do you prepare a sample for UV VIS spectroscopy?
ProcedureTurn on the UV-Vis spectrometer and allow the lamps to warm up for an appropriate period of time (around 20 min) to stabilize them.Fill a cuvette with the solvent for the sample and make sure the outside is clean. ... Place the cuvette in the spectrometer. ... Take a reading for the blank.
Why is UV spectroscopy used in pharmaceutical analysis?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, abou...
What are the applications of spectrophotometry?
In different fields, such as astronomy, molecular biology , chemistry and biochemistry, spectrophotometers are commonly used. Specification applica...
What is the range of UV spectroscopy?
UV-Vis is also considered a general procedure, since in the UV-visible wavelength spectrum, most molecules absorb light. The UV frequency is betwee...
Which lamp is used in UV spectroscopy?
Light with a wavelength range between 190 nm and 800 nm is radiated through the cuvette using a spectrometer and absorption spectrums are recorded....
What is the IR principle?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corr...
What is UV VIS spectroscopy and how does it work?
UV-Vis is a quick , convenient, and inexpensive way of determining the solution concentration of an analyte. In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a so...
What is UV VIS Spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
What is UV Vis?
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV / Vis) in the ultraviolet-visible spectral field refers to absorption spectroscopy ...
What is UV spectrophotometer?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, about the levels of active ingredients present in pharmaceutical compounds.
What wavelength is used to determine the concentration of an analyte?
In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a solution in a cuvette with a wavelength ranging between 180 and 1100 nm. The sample absorbs this UV or visible radiation in the cuvette.
What is the wavelength of UV spectroscopy?
The UV frequency is between 100 and 400 nm, and the visible spectrum is between 400 and 700 nm.
What is the principle of IR spectroscopy?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corresponding structure. The energies depend on the form of the molecular surfaces, the vibronic coupling associated with them and the mass corresponding to the atoms.
What is the radiation from hot solids?
The radiation from typical hot solids consists of several wavelengths and depends primarily on the temperature of the solid and is predictable from the principle of chance, the energy released at each given wavelength. More recently, using a version of this-the tungsten-halogen lamp-has become standard practices.
What is UV visible spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet (UV)-visible spectroscopy is a type of absorption spectroscopy in which UV-visible light is absorbed by the molecule. Absorption of the UV-visible radiations results in the excitation of the electrons from lower to higher energy levels. In organic molecules only certain functional groups (chromophores) that contain valence electrons of low excitation energy can absorb ultraviolet and visible radiation. C-Cyts represent an ideal target molecule for UV-visible spectroscopy because of the large absorption of heme groups. The strong UV-visible absorption bands of the heme originate from the π→π* transitions, providing information about the type of heme, the oxidation, and the spin state of the central iron ion. UV-visible spectroscopy allows in vivo measurements of biofilms under physiologically relevant conditions (Fig. 4D ). In order to detect all the cytochromes (OMCs and inner membrane cytochromes) along the biofilm thickness without any spatial distinction growing the EABs on a transparent electrode (indium tin oxide) is suggested. 78 Moreover, by combining different experimental set-ups is possible to obtain a UV-visible spectrum of the OMCs only confined in the proximity of the electrode surface.
What is UV VIS?
UV–vis is a commonly used technique to characterize nanoparticles. This technique allows to confirm the nanoparticles formation by measuring the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). This procedure can provide information about the size, stability, and aggregation of the NPs [4].
How to measure analyte interactions with MIPs?
UV/Vis spectroscopyis one of the most simplified and economical methods for examining analyte interactions with MIPs where only the change in absorbance is measured as a function of wavelength. The technique is versatile and gives rapid response regarding quantitative information on template binding. Besides pure sensing application, this method is quitesuitable for screening [36]MIPs and choosing the finest polymer composition. With the help of the UV/Vis spectrum, the thorough mechanism of complexation between templates, monomer, and cross-linker during polymerization can also be better understood. It has been observed that after complexation, an absorbance shift toward shorter wavelengths takes place. The procedure makes it easy to compare the spectrum of free template and functional monomer with that of the complex formed. This strategy is equally suitable for monitoring metal polymer complexation in visible regions [37]. Although UV/Vis spectroscopy is not as selective as the fluorescence method, it is nevertheless quite suitable for designing low-cost MIP sensors with moderate sensitivity.
What is FUV spectroscopy used for?
Moreover, FUV spectroscopy can be utilized for qualitative and quantitative analyses of various liquid and solid samples, because each molecule shows a characteristic FUV spectrum with strong absorption, and intensities and wavelengths of FUV bands are very sensitive to changes in concentration, temperature, pH, and so on [ 46–50].
What are the advantages of FUV spectroscopy?
The most fundamental advantage of FUV spectroscopy is that it contains unique information about the electronic transitions and structure of molecules. One can obtain knowledge about them that is not accessible by any other spectroscopy.
Why are C-cyts used in UV spectroscopy?
C-Cyts represent an ideal target molecule for UV-visible spectroscopy because of the large absorption of heme groups. The strong UV-visible absorption bands of the heme originate from the π→π* transitions, providing information about the type of heme, the oxidation, and the spin state of the central iron ion.
How is light absorbed by a sample measured?
The physical principles underlying this method are straightforward, making the instrumentation simple and robust. Light of known wavelength and intensity is directed at the sample and its final intensity, after passing through, is measured by a detector. By comparing the incident radiation (I0) and the transmitted radiation (I), the amount of light absorbed by the sample at that particular wavelength can be easily calculated. Using the Beer–Lambert law, this absorption can be used to measure concentrations of known solutes:
Light source
As a spectrophotometer is a light-based technique, it is a must to choose a steady and bright light source. Basically, the light source of the spectrophotometer should include,
Wavelength selector
The light source that releases a wide range of wavelengths. It is required to select a certain wavelength that suits the sample for examination and analyte for detection. The following are the different methods used for wavelength selection.
Sample analysis
After selecting a certain range of wavelengths, the light is then passed through the sample. Measuring a reference sample is referred to as a “blank sample” in a cuvette
Detection
It is important to convert the light into a readable electronic signal after light passes through the sample and hence there comes the role of detectors. There are different types of detectors used in the spectrophotometer,
What light source is used for UV spectroscopy?
Unfortunately, such a source does not exist. Two different light sources have historically been used in UV-visible spectrophotometers: – The deuterium arc lamp was used to provide a good intensity continuum in the UV region and useful intensity in the visible region – The tungsten-halogen lamp yielded good intensity over the entire visible range and part of the UV spectrum More recently, a single Xenon flash lamp has been used more widely. The use of a Xenon flash lamp as a single source has significant advantages over the use of the two conventional lamps. Deuterium (D
What is the wavelength of a UV spectrophotometer?
Ultraviolet visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometers use a light source to illuminate a sample with light across the UV to the visible wavelength range (typically 190 to 900 nm). The instruments then measure the light absorbed, transmitted, or reflected by the sample at each wavelength. Some spectrophotometers have an extended wavelength range, into the near-infrared (NIR) (800 to 3200 nm).
How does a monochromator work?
To narrow the light down to a selected wavelength band, the light is passed through a monochromator. A monochromator consists of: – An entrance slit, – A dispersion device, to spread the light into different wavelengths (like a rainbow) and allow the selection of a nominated band of wavelengths, and – An exit slit where the light of the nominated wavelengths passes through and onto the sample. An easy way to think about a monochromator is to think of a room, with the sun shining through a window. The sunlight hits a prism that separates the white light into a rainbow. The rainbow falls onto a window on the opposite side of the room. As the prism is turned, light of different colors i.e. different wavelengths, pass out of the room through the window. Ideally, the output from a monochromator is light of a single wavelength. In practice, however, the output is always a band of wavelengths. Most spectrophotometers on the market today contain holographic gratings as the dispersion device. These optical components are made from glass, onto which extremely narrow grooves are precisely etched onto the surface. The dimensions of the grooves are of the same order as the wavelength of light to be dispersed. Finally, an aluminum coating is applied to create a reflective surface. Interference and diffraction of the light falling on the grating is reflected at different angles, depending on the wavelength. Holographic gratings yield a linear angular dispersion with wavelength and are temperature insensitive. However, they reflect light in different orders, which overlap (see Figure 12). As a result, filters must be used to ensure that only the light from the desired reflection order reaches the detector. A concave grating disperses and focuses light simultaneously.
What is a single monochromator spectrophotometer?
A single monochromator spectrophotometer is used for general-purpose spectroscopy and can be integrated into a compact optical system. Figure 13 shows a schematic diagram of a single monochromator optical system. A single monochromator spectrophotometer cannot select the wavelengths of light as narrowly as a double monochromator system, but this ability may not be required for many applications, for example when measuring samples that have broad absorption peaks.
What wavelength of light is used to transfer electrons from the oxygen atom to the C-O bond?
Figure 2. Electronic transitions in formaldehyde. UV light at 187 nm causes excitation of an electron in the C-O bond and light at 285 nm wavelength causes excitation and transfer of an electron from the oxygen atom to the C-O bond.
How to determine the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation?
Because radiation acts as a wave, it can be classified in terms of either waveleng th or frequency, which are related by the following equation: ν = c/λ where ν is frequency (in seconds), c is the speed of light (3 × 108ms-1), and λ is wavelength (in meters). In UV-Vis spectroscopy, wavelength is usually expressed in nanometers (1 nm = 10-9m). It follows from the equations that radiation with shorter wavelength has higher energy, and, for UV-Vis spectroscopy, the low (short)
What happens when radiation interacts with matter?
When radiation interacts with matter, several processes can occur, including reflection, scattering, absorbance, fluorescence/ phosphorescence (absorption and re-emission), and photochemical reactions (absorbance and bond breaking). Typically, when measuring samples to determine their UV-visible spectrum, absorbance is measured. Because light is a form of energy, absorption of light by matter causes the energy content of the molecules (or atoms) in the matter to increase. The total potential energy of a molecule is represented as the sum of its electronic, vibrational, and rotational energies:

How Does Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Work?
- To give you a better understanding of how Uv-Vis spectroscopy works, let’s talk about its main components and the processes of how light is absorbed and measured by the spectrometer.
The Purpose and Applications of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy has been widely used in various sample testing today. This technique has the following famous innovative applications:
Advantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The best advantage of utilizing Uv-Vis spectrometers is their optimal accuracy. These machines are guaranteed to give you accurate readings, which are essential when you need to prepare chemical solutions or record the movement of the celestial bodies. Uv-Vis spectroscopy is also easy to understand with its simple analysis ability. The spectrometers are convenient and easy t…
Disadvantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The main disadvantage of Uv-Vis spectrometers is their challenging assembly, and it may take time to prepare using them. Ensure that the area where you’ll place the device is clear of any electronic noise, outside light, and other contaminants that could affect the measurements and readings of the spectrometer. A Uv-Vis spectrometer is sensitive to external factors, so you mus…
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Limitations
- Even an advanced technique like Uv-Vis spectroscopy has limitations, too. You can grasp what these are below:
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Is The Future
- UV-vis spectroscopy provides researchers and scientists with more efficient methods to measure light wavelengths, providing accurate readings that are helpful in various biological and chemical analyses. The UV-vis spectrometer device is precise and easy to operate, provided that you maintain a clean working area free from any external noise and dust that can affect the machine’…