What does a UV-Vis spectrum show?
- The x-axis (horizontal) shows the wavelength.
- The y-axis (vertical) shows the dependent variable; the absorbance.
Full Answer
What is the UV Vis spectrum?
UV-vis spectroscopy is a cost-effective, simple, versatile, non-destructive, analytical technique suitable for a large spectrum of organic compounds and some inorganic species. As a function of wavelength, UV-vis spectrophotometers measure the absorption or transmission of light that passes through a medium. In order to classify and measure the ...
What are some uses of UV/Vis spectroscopy?
13.21.1.1: Some Uses of UV/Vis Spectroscopy
- Electronic transitions. Let's take as our first example the simple case of molecular hydrogen, H 2. ...
- Looking at UV-vis spectra. We have been talking in general terms about how molecules absorb UV and visible light - now let's look at some actual examples of data from ...
- Applications of UV spectroscopy in organic and biological chemistry
What is maximum absorbance wavelength?
What is maximum absorbance wavelength? The absorption is highest at around 510 nm (the wavelength at which absorption reaches its peak is called absorption maximum wavelength). How is the UV absorption maximum of paracetamol determined? A UV absorption maximum was determined by scanning 10µg/ml solution of paracetamol in phosphate buffer 6.8, in between 200-400 nm by using UV-visible spectrophotometer.
What is ultraviolet visible spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent ranges.

How do you read UV absorbance spectrum?
1) Step 1: Identify the number of peaks appearing in the UV-VIS spectrum. Figure 5 shows several peaks indicating the presence of an excited electron. The easier the electrons are excited, the greater the wavelength that is absorbed, the more electrons are excited, the higher the absorbance.
What does UV-Vis spectra tell you?
UV-Vis Spectroscopy (or Spectrophotometry) is a quantitative technique used to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light. This is done by measuring the intensity of light that passes through a sample with respect to the intensity of light through a reference sample or blank.
How do you explain UV-Vis graph?
0:292:11How to Interpret a UV Vis Graph - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipDifferent colors are seen. So at about 400 nanometers blue or violet light is absorbed and on theMoreDifferent colors are seen. So at about 400 nanometers blue or violet light is absorbed and on the other end of the spectrum at 700 nanometers red light is absorbs. And every other color is in between.
How do you read a absorbance graph?
2:425:23Spectrophotometer: Absorbance Curves - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then you draw the line from the curve these dotted lines from the curve to meet your x axisMoreAnd then you draw the line from the curve these dotted lines from the curve to meet your x axis which is going to give you the concentration.
How can you tell the color of an absorption spectrum?
If wavelengths of light from a certain region of the spectrum are absorbed by a material, then the materials will appear to be the complementary color Thus, for instance, if violet light with wavelength of 400nm is absorbed, the material will look yellow. If the material absorbs blue you will see the color orange.
Why are the peaks in UV spectrum broad?
In UV-Visible spectra Bonds will be in constant vibration, this variation will absorb nearby energies i.e, ΔE , for this reason UV peaks are broader. Spectrum is broaden by spontaneous emission.
How do you calculate particle size from UV-Vis?
0:567:41How to estimate the size of nanoparticles from UV-Vis ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe diameter of the smallest hydrogen atom is 0.074 nanometer and that of the relatively. Large leadMoreThe diameter of the smallest hydrogen atom is 0.074 nanometer and that of the relatively. Large lead atom having atomic number 82 is 0.35 nanometer from these sizes.
What do absorbance readings mean?
Absorbance is a measure of the quantity of light absorbed by a sample. It is also known as optical density, extinction, or decadic absorbance. The property is measured using spectroscopy, particularly for quantitative analysis.
What does high absorbance mean in spectrophotometry?
When you get very high absorbance (>1.5), it means that most of the light are absorbed by the sample and only small amount of the light detected by detector.
What does absorbance tell you about concentration?
One factor that influences the absorbance of a sample is the concentration (c). The expectation would be that, as the concentration goes up, more radiation is absorbed and the absorbance goes up. Therefore, the absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration.
What is the UV absorbance of 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one?
The conjugated pi system in 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one gives rise to a strong UV absorbance at 236 nm due to a π - π * transition. However, this molecule also absorbs at 314 nm. This second absorbance is due to the transition of a non-bonding (lone pair) electron on the oxygen up to a π * antibonding MO:
What is the absorbance of 260 nm?
You can see that the absorbance value at 260 nm (A 260) is about 1.0 in this spectrum.
When a double-bonded molecule such as ethene absorbs light, it undergoes?
When a double-bonded molecule such as ethene (common name ethylene) absorbs light, it undergoes a π - π* transition. Because π - π * energy gaps are narrower than σ - σ* gaps, ethene absorbs light at 165 nm - a longer wavelength than molecular hydrogen.
What happens to the energy gap of conjugated pi systems?
As conjugated pi systems become larger, the energy gap for a π - π * transition becomes increasingly narrow, and the wavelength of light absorbed correspondingly becomes longer. The absorbance due to the π - π * transition in 1,3,5-hexatriene, for example, occurs at 258 nm, corresponding to a Δ E of 111 kcal/mol.
What wavelength do UV cameras use?
more. UV cameras use light in the near UV region (200 – 380 nm). Special filters block the visible and IR wavelengths and let the UV through. The lenses are made of quartz or fluorite, because glass is opaque to UV.
What does black light look like?
A black light looks dark purple, but most of the light it emits is in the ultraviolet (UV) range. Under a UV light, white clothes and UV paints emit a bright glow. They all contain phosphors — substance that absorb UV energy and re-emit it as visible light. Comment on Ernest Zinck's post “UV cameras use light in t...”.
Does a compound absorb light?
Not necessarily, if the compound only has effect on UV light then it neither absorbs nor reflects visible light ( like most amorphous substances). Also if the compound absorbs a photon it will usually then release that energy shortly after, the released photon will most likely be a wavelength in the UV spectrum.
How many nm does an absorption spectrometer have?
An absorption spectrometer works in a range from about 200 nm (in the near ultra-violet) to about 800 nm (in the very near infra-red). Only a limited number of the possible electron jumps absorb light in that region.
Why does absorption take place over a range of wavelengths?
This problem arises because rotations and vibrations in the molecule are continually changing the energies of the orbitals - and that, of course, means that the gaps between them are continually changing as well. The result is that absorption takes place over a range of wavelengths rather than at one fixed one.
How many orbitals does buta-1,3-diene have?
In buta-1,3-diene, there are two pi bonding orbitals and two pi anti-bonding orbitals. This is all discussed in detail on the introductory page that you should have read. The highest occupied molecular orbital is often referred to as the HOMO - in these cases, it is a pi bonding orbital.
What happens to the energy of each wavelength of light?
If that particular amount of energy is just right for making one of these energy jumps, then that wavelength will be absorbed - its energy will have been used in promoting an electron.
Why does the graph look like it does with a broad absorption peak rather than a single line at 217?
If you are really wide-awake you might wonder why the graph looks like it does with a broad absorption peak rather than a single line at 217 nm. A jump from a pi bonding orbital to a pi anti-bonding orbital ought to have a fixed energy and therefore absorb a fixed wavelength. The compound is in fact absorbing over a whole range of wavelengths suggesting a whole range of energy jumps.
What wavelength do jumps absorb?
The jumps shown with grey dotted arrows absorb UV light of wavelength less that 200 nm.
What do the grey dotted arrows on the spectrum show?
The grey dotted arrows show jumps which absorb light outside the region of the spectrum we are working in.
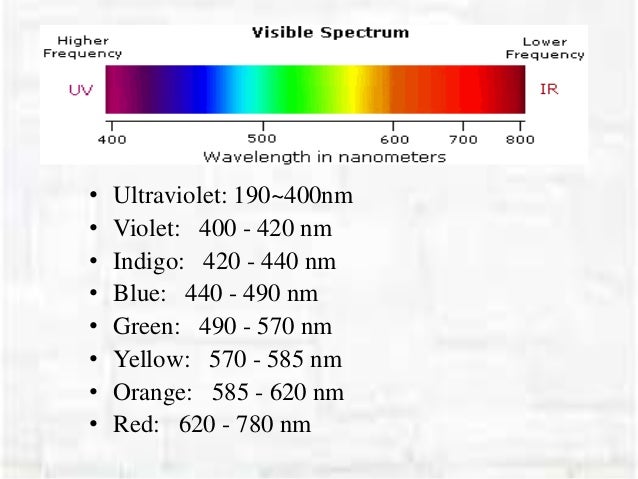
What is the longest visible wavelength?
The longest visible wavelength is red and the shortest is violet. Other common colors of the spectrum, in order of decreasing wavelength, may be remembered by the mnemonic: ROY G BIV. The wavelengths of what we perceive as particular colors in the visible portion of the spectrum are displayed and listed below.
What wavelength is chromophores detected?
The presence of chromophores in a molecule is best documented by UV-Visible spectroscopy, but the failure of most instruments to provide absorption data for wavelengths below 200 nm makes the detection of isolated chromophores problematic.
Why is it important to correct the absorbance value?
Because the absorbance of a sample will be proportional to the number of absorbing molecules in the spectrometer light beam (e.g. their molar concentration in the sample tube), it is necessary to correct the absorbance value for this and other operational factors if the spectra of different compounds are to be compared in a meaningful way. The corrected absorption value is called "molar absorptivity", and is particularly useful when comparing the spectra of different compounds and determining the relative strength of light absorbing functions (chromophores). Molar absorptivity (ε) is defined as:
What is the wavelength of a wave?
Visible wavelengths cover a range from approximately 400 to 800 nm. The longest visible wavelength is red and the shortest is violet.
When a sample molecules are exposed to light having an energy that matches a possible electronic transition within the molecule,?
When sample molecules are exposed to light having an energy that matches a possible electronic transition within the molecule, some of the light energy will be absorbed as the electron is promoted to a higher energy orbital.
Can radiation be seen?
Most of the radiation that surrounds us cannot be seen, but can be detected by dedicated sensing instruments. This electromagnetic spectrum ranges from very short wavelengths (including gamma and x-rays) to very long wavelengths (including microwaves and broadcast radio waves).
Is visible light a wave?
Electromagnetic radiation such as visible light is commonly treated as a wave phenomenon, characterized by a wavelength or frequency. Wavelength is defined on the left below, as the distance between adjacent peaks (or troughs), and may be designated in meters, centimeters or nanometers (10 -9 meters). Frequency is the number of wave cycles that ...
