
How do you read the UV-VIS spectroscopy spectrum? To read the UV-vis spectrum the graph is plotted between the wavelength and the absorption. The wavelength at which maximum absorption occurs is called the λ max .
What is UV Vis spectroscopy?
What is UV VIS Spectroscopy? Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region.
How many peaks does a UV-Vis spectrum have?
You’ll notice that this UV spectrum is much simpler than the IR spectra we saw earlier: this one has only one peak, although many molecules have more than one. Notice also that the convention in UV-vis spectroscopy is to show the baseline at the bottom of the graph with the peaks pointing up.
What is the convention in UV-Vis spectroscopy?
Notice also that the convention in UV-vis spectroscopy is to show the baseline at the bottom of the graph with the peaks pointing up. Wavelength values on the x-axis are generally measured in nanometers (nm) rather than in cm -1 as is the convention in IR spectroscopy.
What is UV-VIS/ultraviolet/visible area (UV-Vis)?
Ultraviolet / Visible Area (UV-VIS) measurements span wavelengths from around 200 nm to 800 nm. The absorption by a molecule of ultraviolet or visible radiation results in transitions between the molecule’s electrical energy levels.

How do you read a absorbance graph?
2:425:23Spectrophotometer: Absorbance Curves - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd then you draw the line from the curve these dotted lines from the curve to meet your x axisMoreAnd then you draw the line from the curve these dotted lines from the curve to meet your x axis which is going to give you the concentration.
How do you read an absorbance spectrum graph What does it mean?
The higher the value, the more of a particular wavelength is being absorbed. You will see that absorption peaks at a value of 217 nm. This is in the ultra-violet and so there would be no visible sign of any light being absorbed - buta-1,3-diene is colourless. You read the symbol on the graph as "lambda-max".
What do peaks in UV-Vis mean?
Many organic compounds give more than one maximum peak when its UV-Vis spectra is analyzed. Each peak correspond to a electron transition from a ground state to an excited state, and more than one different transitions (with different energy, and therefore, different wavelenght) are allowed.
What does UV-Vis absorbance tell you?
UV-Vis Spectroscopy (or Spectrophotometry) is a quantitative technique used to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light. This is done by measuring the intensity of light that passes through a sample with respect to the intensity of light through a reference sample or blank.
How do you read a color spectrum?
4:5411:11Visible Light Spectrum Explained - Wavelength Range / Color Chart ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipGreen light ranges from 500 to about 570.. And yellow is very small it's 570 to 590. The range isMoreGreen light ranges from 500 to about 570.. And yellow is very small it's 570 to 590. The range is limited orange goes up from like 590 to 620. So red is from 620 to 700.
How do you tell the color from the absorbance spectrum?
If wavelengths of light from a certain region of the spectrum are absorbed by a material, then the materials will appear to be the complementary color Thus, for instance, if violet light with wavelength of 400nm is absorbed, the material will look yellow. If the material absorbs blue you will see the color orange.
How do you find the lambda max of a graph?
1:041:43How to Plot Lambda max - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can drag it anywhere and you can move it like this then you have to click on maximum point toMoreYou can drag it anywhere and you can move it like this then you have to click on maximum point to know the lambda maximum then you have to click the utmost point of the plot.
How are wavelength and absorbance related?
One important consideration is the wavelength of radiation to use for the measurement. Remember that the higher the molar absorptivity, the higher the absorbance. What this also means is that the higher the molar absorptivity, the lower the concentration of species that still gives a measurable absorbance value.
What does a UV-Vis spectrophotometer measure?
What does a UV-Vis spectrophotometer measure? UV-Vis and UV-Vis-NIR instruments measure the light absorbed, transmitted, or reflected by the sample across a certain wavelength range.
How can you tell if UV is active?
Ones that do are said to be “UV-active” and ones that do not are “UV- inactive.” To be UV-active, compounds must possess a certain degree of conjugation, which occurs most commonly in aromatic compounds. One can then outline the spots with a pencil, while under the UV light, to mark their location.
Why are UV-Vis peaks broad?
In UV-Visible spectra Bonds will be in constant vibration, this variation will absorb nearby energies i.e, ΔE , for this reason UV peaks are broader. Spectrum is broaden by spontaneous emission. However, spontaneous emission is related to energy of transition.
What wavelengths are visible light?
The visible wavelengths cover a range from approximately 0.4 to 0.7 µm. The longest visible wavelength is red and the shortest is violet. Common wavelengths of what we perceive as particular colours from the visible portion of the spectrum are listed below.
What does a high absorbance value mean?
Absorbance values greater than or equal to 1.0 are too high. If you are getting absorbance values of 1.0 or above, your solution is too concentrated. Simply dilute your sample and recollect data . Keep in mind that absorbance is the logarithm of the transmission (T) of light through a sample.
What you mean by absorbance?
Absorbance (A), also known as optical density (OD), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. Transmittance is the quantity of light that passes through a solution.
How do you read a standard curve graph?
3:046:51What is a Standard Curve? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThen you're going to measure the absorbance of those solutions in the spectrophotometer. Then you'reMoreThen you're going to measure the absorbance of those solutions in the spectrophotometer. Then you're going to make a graph of concentration versus absorbance that is called the standard curve.
How does absorbance relate to wavelength?
Molecules will have a certain range of absorbance with a peak at a certain point. A wavelength longer than the peak absorbance and shorter than the peak absorbance will result in more light being recorded by the detector.
Why is UV spectroscopy used in pharmaceutical analysis?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, abou...
What are the applications of spectrophotometry?
In different fields, such as astronomy, molecular biology , chemistry and biochemistry, spectrophotometers are commonly used. Specification applica...
What is the range of UV spectroscopy?
UV-Vis is also considered a general procedure, since in the UV-visible wavelength spectrum, most molecules absorb light. The UV frequency is betwee...
Which lamp is used in UV spectroscopy?
Light with a wavelength range between 190 nm and 800 nm is radiated through the cuvette using a spectrometer and absorption spectrums are recorded....
What is the IR principle?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corr...
What is UV VIS spectroscopy and how does it work?
UV-Vis is a quick , convenient, and inexpensive way of determining the solution concentration of an analyte. In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a so...
What is UV spectroscopy?
UV-VIS (ultraviolet-visible) spectroscopy or spectrophotometry is the study of the interaction of light with matter at electronic levels. It ranges from the vacuum level ultraviolet region i.e. 180nm to visible region i.e. 780nm. UV spectrum extends from 180nm to 400nm whereas the visible region ranges from 400nm to 780nm.
What is the most commonly used detector in UV visible spectroscopy?
The most commonly used detector in UV visible spectroscopy is a photomultiplier tube. Repetition of the dynode is structured with a slight potential difference at a particular angle. The incoming photon strikes the cathode, after knocking out several electrons from the dynodes every time.
How does a single beam spectrophotometer work?
Single beam uv-vis spectrophotometer has a single beam as the name indicates. The incident light coming from the source is passed through a monochromator then that incident monochromatic light moves through a slit. Then it passes through the sample solution. Where some of the incident light is absorbed by the sample while other is transmitted. That transmitted light is detected by the detector. The detected light is then amplified, recorded, and then displayed on a suitable readout device. Spectrum is plotted and the λ max is located.
What does zero mean in UV spectroscopy?
The zero in UV spectroscopy indicates the total transmittance while baseline is the amount of radiation absorbed by the cuvette and the sample solution.
What material is used in ultraviolet spectroscopy?
Fused silica and quartz cuvettes are most commonly used in ultraviolet spectroscopy as they are transparent in the ultraviolet region i.e. quartz can not absorb ultraviolet light so are used in ultraviolet spectrophotometers. Plastic and glass materials absorb ultraviolet light which interferes with the results.
Why does fluorescence have a negative absorption value?
The negative value of absorption indicates that the sample is having an impurity in it, which causes interference with the result. The fluorescence caused by the impurity can enhance the value of transmitted radiation as compared to incident radiation. That is the reason it gives a negative absorption value.
What is the transition of electrons at different levels by absorption of radiation from ultraviolet to visible region?
This line graph of various absorptivities on specific levels of radiations is because of the absorption capacities of compounds at certain levels. These levels are called regions of absorption and the compounds are termed as chromophores.
What is UV Vis?
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV / Vis) in the ultraviolet-visible spectral field refers to absorption spectroscopy ...
What is UV VIS Spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
What is UV spectrophotometer?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, about the levels of active ingredients present in pharmaceutical compounds.
What wavelength is used to determine the concentration of an analyte?
In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a solution in a cuvette with a wavelength ranging between 180 and 1100 nm. The sample absorbs this UV or visible radiation in the cuvette.
What is the wavelength of UV spectroscopy?
The UV frequency is between 100 and 400 nm, and the visible spectrum is between 400 and 700 nm.
What is the principle of IR spectroscopy?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corresponding structure. The energies depend on the form of the molecular surfaces, the vibronic coupling associated with them and the mass corresponding to the atoms.
What is the radiation from hot solids?
The radiation from typical hot solids consists of several wavelengths and depends primarily on the temperature of the solid and is predictable from the principle of chance, the energy released at each given wavelength. More recently, using a version of this-the tungsten-halogen lamp-has become standard practices.
How to move between peaks in a spectrum diagram?
You can move between the peaks lines: select spectrum of interest (see Available spectra fig.) and click on the spectrum diagram, use the left/right keyboard cursor to move between the peaks . The current peak will be selected with the peak cursor (see fig.) directly on the diagram and in the Calculated Spectrum peaks list (see fig.). Besides the corresponding transitions between MOs will be shown on the molecular orbitals diagram and the line intensities of these transitions will be in correspondence with the magnitudes of the contribution to the excited state under consideration.
How to show spectrum analysis?
To show the Analyze Spectrum window click the menu Tools --> Analyze Spectrum .
How to edit diagram text?
To edit the diagram Title and Foot text double click it with the mouse left button and start editing the text.
How to select the energy range in a diagram?
To select the custom energy range (wavelength range) for your diagram use the menu View-->Set energy range .
What is the use of spectrum tool?
Use the Analyze spectrum tool for analyzing the calculated spectra, graphical editing it and adding experimental ones.
What is the UV absorbance of 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one?
The conjugated pi system in 4-methyl-3-penten-2-one gives rise to a strong UV absorbance at 236 nm due to a π - π * transition. However, this molecule also absorbs at 314 nm. This second absorbance is due to the transition of a non-bonding (lone pair) electron on the oxygen up to a π * antibonding MO:
What happens to the energy gap of conjugated pi systems?
As conjugated pi systems become larger, the energy gap for a π - π * transition becomes increasingly narrow, and the wavelength of light absorbed correspondingly becomes longer. The absorbance due to the π - π * transition in 1,3,5-hexatriene, for example, occurs at 258 nm, corresponding to a Δ E of 111 kcal/mol.
What is the absorbance of 260 nm?
You can see that the absorbance value at 260 nm (A 260) is about 1.0 in this spectrum.
When a double-bonded molecule such as ethene absorbs light, it undergoes?
When a double-bonded molecule such as ethene (common name ethylene) absorbs light, it undergoes a π - π* transition. Because π - π * energy gaps are narrower than σ - σ* gaps, ethene absorbs light at 165 nm - a longer wavelength than molecular hydrogen.
What is the longest visible wavelength?
The longest visible wavelength is red and the shortest is violet. Other common colors of the spectrum, in order of decreasing wavelength, may be remembered by the mnemonic: ROY G BIV. The wavelengths of what we perceive as particular colors in the visible portion of the spectrum are displayed and listed below.
What wavelength is chromophores detected?
The presence of chromophores in a molecule is best documented by UV-Visible spectroscopy, but the failure of most instruments to provide absorption data for wavelengths below 200 nm makes the detection of isolated chromophores problematic.
Why is it important to correct the absorbance value?
Because the absorbance of a sample will be proportional to the number of absorbing molecules in the spectrometer light beam (e.g. their molar concentration in the sample tube), it is necessary to correct the absorbance value for this and other operational factors if the spectra of different compounds are to be compared in a meaningful way. The corrected absorption value is called "molar absorptivity", and is particularly useful when comparing the spectra of different compounds and determining the relative strength of light absorbing functions (chromophores). Molar absorptivity (ε) is defined as:
What is the wavelength of a wave?
Visible wavelengths cover a range from approximately 400 to 800 nm. The longest visible wavelength is red and the shortest is violet.
When a sample molecules are exposed to light having an energy that matches a possible electronic transition within the molecule,?
When sample molecules are exposed to light having an energy that matches a possible electronic transition within the molecule, some of the light energy will be absorbed as the electron is promoted to a higher energy orbital.
Is visible light a wave?
Electromagnetic radiation such as visible light is commonly treated as a wave phenomenon, characterized by a wavelength or frequency. Wavelength is defined on the left below, as the distance between adjacent peaks (or troughs), and may be designated in meters, centimeters or nanometers (10 -9 meters). Frequency is the number of wave cycles that ...
Is sunlight a color?
Although we see sunlight (or white light) as uniform or homogeneous in color, it is actually composed of a broad range of radiation wave lengths in the ultraviolet (UV), visible and infrared (IR ) portions of the spectrum.
Why does the graph look like it does with a broad absorption peak rather than a single line at 217?
If you are really wide-awake you might wonder why the graph looks like it does with a broad absorption peak rather than a single line at 217 nm. A jump from a pi bonding orbital to a pi anti-bonding orbital ought to have a fixed energy and therefore absorb a fixed wavelength. The compound is in fact absorbing over a whole range of wavelengths suggesting a whole range of energy jumps.
What wavelength do jumps absorb?
The jumps shown with grey dotted arrows absorb UV light of wavelength less that 200 nm.
What happens to the energy of each wavelength of light?
If that particular amount of energy is just right for making one of these energy jumps, then that wavelength will be absorbed - its energy will have been used in promoting an electron.
Why does absorption take place over a range of wavelengths?
This problem arises because rotations and vibrations in the molecule are continually changing the energies of the orbitals - and that, of course, means that the gaps between them are continually changing as well. The result is that absorption takes place over a range of wavelengths rather than at one fixed one.
What do the grey dotted arrows on the spectrum show?
The grey dotted arrows show jumps which absorb light outside the region of the spectrum we are working in.
How many nm does an absorption spectrometer have?
An absorption spectrometer works in a range from about 200 nm (in the near ultra-violet) to about 800 nm (in the very near infra-red). Only a limited number of the possible electron jumps absorb light in that region.
How many orbitals does buta-1,3-diene have?
In buta-1,3-diene, there are two pi bonding orbitals and two pi anti-bonding orbitals. This is all discussed in detail on the introductory page that you should have read. The highest occupied molecular orbital is often referred to as the HOMO - in these cases, it is a pi bonding orbital.
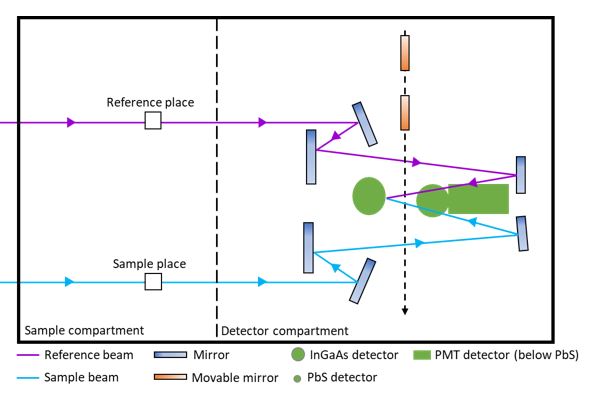
Uv-Visible Spectroscopy
Lambert Law
Beer Law
Beer-Lambert Law
Instrumentation of Uv-Visible Spectroscopy
Spectral Analysis in Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- UV-VIS spectrum is a graph that shows absorption at different wavelengths. The relative maxima are known as lambda max (λmax). Spectra obtained by such techniques can be useful for extracting information such as purity and composition. UV-Vis spectroscopic spectra are frequently utilized to check the presence of different organic and conjugated che...
Shifting of Absorption Band and Change in Intensity
Types of Uv-Vis Spectrometers
Applications of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
Concepts Berg