
Ultraviolet Visible Spectrophotometry
- SPECTROPHOTOMETRY | Biochemical Applications. Ultraviolet (UV)–visible spectrophotometry is widely used in biochemistry, both for the determination of species and for studying biochemical processes.
- SPECTROPHOTOMETRY | Overview. ...
- CHROMIUM. ...
- Calcium Carbonate. ...
- Light and Matter. ...
- SPECTROPHOTOMETRY | Organic Compounds
What are some uses of UV/Vis spectroscopy?
13.21.1.1: Some Uses of UV/Vis Spectroscopy
- Electronic transitions. Let's take as our first example the simple case of molecular hydrogen, H 2. ...
- Looking at UV-vis spectra. We have been talking in general terms about how molecules absorb UV and visible light - now let's look at some actual examples of data from ...
- Applications of UV spectroscopy in organic and biological chemistry
Which spectrophotometer is the best?
Spectrophotometer DNA is an analytical instrument that can be used to measure the nucleic acid of a substance. Other instruments in this category include the NIR spectrophotometer which is considered by some experts as the best spectrophotometer in the world today. This is because of its accuracy and features.
What is a colorimeter vs. spectrophotometer?
• Colorimetry uses fixed wavelengths, which are in the visible range only, but spectrophotometry can use wavelengths in a wider range (UV and IR also). • Colorimeter measures the absorbance of light, whereas the spectrophotometer measures the amount of light that passes through the sample.
What is a cuvette blanked in a spectrophotometer?
“A blank cuvette is used to calibrate the spectrophotometer readings: they document the baseline response of the environment-instrument-sample system. It is analogous to “zeroing” a scale before weighing. Running a blank allows you to document the influence of the particular instrument on your readings.”
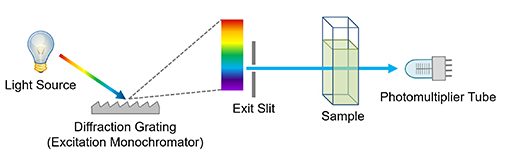
How does UV spectrophotometer measure absorbance?
Ultraviolet visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometers use a light source to illuminate a sample with light across the UV to the visible wavelength range (typically 190 to 900 nm). The instruments then measure the light absorbed, transmitted, or reflected by the sample at each wavelength.
What is actually measured by UV-Vis absorption instrument?
A UV Vis spectrophotometer is an instrument designed to measure the absorbance in the UV Vis region using the Beer-Lambert law. It measures the intensity of light passing through a sample solution in a cuvette and compares it to the intensity of the light before it passes through the sample.
What kind of information can you get from UV spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy is a widely used technique in many areas of science ranging from bacterial culturing, drug identification and nucleic acid purity checks and quantitation, to quality control in the beverage industry and chemical research.
What does a spectrophotometer directly measure?
Spectrophotometers measure absorbance (A) and transmittance (T). The intensity of light (I0) measures photons per second. When light passes through a blank sample, it does not absorb light so is symbolised as (I).
Why is UV spectroscopy used in pharmaceutical analysis?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, abou...
What are the applications of spectrophotometry?
In different fields, such as astronomy, molecular biology , chemistry and biochemistry, spectrophotometers are commonly used. Specification applica...
What is the range of UV spectroscopy?
UV-Vis is also considered a general procedure, since in the UV-visible wavelength spectrum, most molecules absorb light. The UV frequency is betwee...
Which lamp is used in UV spectroscopy?
Light with a wavelength range between 190 nm and 800 nm is radiated through the cuvette using a spectrometer and absorption spectrums are recorded....
What is the IR principle?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corr...
What is UV VIS spectroscopy and how does it work?
UV-Vis is a quick , convenient, and inexpensive way of determining the solution concentration of an analyte. In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a so...
What is UV VIS Spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
What is UV spectrophotometer?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, about the levels of active ingredients present in pharmaceutical compounds.
What is UV Vis?
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV / Vis) in the ultraviolet-visible spectral field refers to absorption spectroscopy ...
What wavelength is used to determine the concentration of an analyte?
In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a solution in a cuvette with a wavelength ranging between 180 and 1100 nm. The sample absorbs this UV or visible radiation in the cuvette.
What is the wavelength of UV spectroscopy?
The UV frequency is between 100 and 400 nm, and the visible spectrum is between 400 and 700 nm.
What is the principle of IR spectroscopy?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corresponding structure. The energies depend on the form of the molecular surfaces, the vibronic coupling associated with them and the mass corresponding to the atoms.
Where are UV visible spectrophotometers used?
UV-Visible Mid-range to Upper-end Spectrophotometers are typically used in research laboratories, including university and industrial laboratories.
Light source
As a spectrophotometer is a light-based technique, it is a must to choose a steady and bright light source. Basically, the light source of the spectrophotometer should include,
Wavelength selector
The light source that releases a wide range of wavelengths. It is required to select a certain wavelength that suits the sample for examination and analyte for detection. The following are the different methods used for wavelength selection.
Sample analysis
After selecting a certain range of wavelengths, the light is then passed through the sample. Measuring a reference sample is referred to as a “blank sample” in a cuvette
Detection
It is important to convert the light into a readable electronic signal after light passes through the sample and hence there comes the role of detectors. There are different types of detectors used in the spectrophotometer,
What is UV spectroscopy?
UV Vis spectroscopy is a type of absorption spectroscopy in which a sample is illuminated with electromagnetic rays of various wavelengths in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible (Vis) ranges. Depending on the substance, the UV or visible light rays are partially absorbed by the sample. The remaining light, i.e. the transmitted light, is recorded as a function of wavelength by a suitable detector. The detector then produces the sample's unique UV Vis spectrum (also known as the absorption spectrum).
Why is the sample compartment open in UV spectrophotometers?
The sample compartment in UV Vis array spectrophotometers is open due to the fact that array instruments use reverse optics and the simultaneous detection of all wavelengths of the spectrum.
How to measure transmittance in a spectrophotometer?
In a spectrophotometer the transmittance is measured by dividing the intensity spectrum of light transmitted through a sample (I) by the intensity spectrum of light transmitted through the blank (I 0 ).
How to analyze a compound with UV spectroscopy?
Molecules can be analyzed using UV Vis spectroscopy if they possess any functional group or conjugation, or if they produce a color complex. As inorganic compounds do not contain any functional group or conjugation, the common method for analyzing them is by reaction with a suitable compound. This produces a color complex whose absorbance can be photometrically measured in the visible region and correlated with its actual concentration. For example, iron is commonly analyzed by a reaction with 1, 10-phenthroline to produce a red color complex. The absorbance of the complex is measured at 570 nm to estimate iron concentration.
What happens to the absorption of UV light?
The absorption of UV light results in electronic transitions from lower energy levels to higher energy levels. Absorption of ultraviolet radiation in organic molecules is restricted to certain functional groups (chromophores) that contain valence electrons of low excitation energy. The molecular transitions/interactions that take place due to UV absorption are:
What are the different types of spectroscopic techniques?
The spectroscopic techniques commonly used for chemical analysis are atomic spectroscopy, ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy (UV Vis spectroscopy), infrared spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance .
What is UV/VIS spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet and visible light range (UV/VIS) is widely applied in research, production and quality control for the classification and study of substances. UV/VIS spectroscopy is based on the absorption of light by a sample. Depending on the amount of light and its wavelength absorbed by the sample, valuable information can be obtained, such as the purity of the sample. Moreover, the amount of absorbed light is related to the amount of sample, and thus, quantitative analysis is possible by optical spectroscopy. This article more specifically explores techniques when using a spectrophotometer to determine concentration of an analyte. A UV/VIS spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light passing through a sample solution in a cuvette, and compares it to the intensity of the light before it passes through the sample. The main components of a UV/VIS spectrophotometer are a light source, a sample holder, a dispersive device to separate the different wavelengths of the light and a suitable detector. This instrument measures Transmittance which is the ratio of the transmitted intensity I to the original intensity of light. An important derived (calculated) variable also reported by the instrument is the Absorbance which is defined as A = −log (Transmittance).
When using a spectrophotometer to determine concentration of a sample solution of unknown concentration by UV/VIS?
When using a spectrophotometer to determine concentration of a sample solution of unknown concentration by UV/VIS spectroscopy, a calibration line must first be created . This is done by measuring the light absorption of several standard solutions of different , known concentrations at a predefined, fixed wavelength. The below calibration line is obtained:
How do scanning spectrophotometers measure transmittance?
The grating is rotated in order to individually select each wavelength that is then sent through a cuvette. The transmittance at this specific wavelength is recorded. The whole spectrum is obtained by continuously changing the wavelength of light (i.e. scanning) incoming onto the sample solution by rotating the grating. Alternately, in Array Spectrophotometers, the sample is illuminated by a light beam consisting of all spectral components of the UV/ VIS range. The sample in the cuvette absorbs all wavelengths simultaneously and the transmitted light is diffracted and then detected by a CCD sensor. Measuring the whole UV/VIS spectrum is generally faster than using a conventional scanning spectrophotometer since the spectrum is recorded simultaneously at all wavelengths. Moreover, an array detector has an integrating function which accumulates individual measurements to enhance the signal, leading to a strongly increased signal to noise ratio, and thus to an improved signal quality of the measured spectrum. Array Spectrophotometers present an innovative approach to speed up full spectrum scan based on reverse optics technology. The robust design without any moving optical parts ensures very good optical performance.
What is the wavelength of a Xenon flash lamp?
The light source consists of a Xenon flash lamp for the ultraviolet (UV) as well as for the visible (VIS) and near-infrared wavelength regions covering a spectral range from 190 up to 1100 nm. The lamp flashes are focused on a glass fiber which drives the beam of light onto a cuvette containing the sample solution.
Is UV absorbance a function of wavelength?
Absorbance as a function of wavelength. In general, a UV/VIS spectrum is graphically represented as absorbance as a function of wavelength. The advantage of this representation is obvious; the height of the absorption peaks is directly proportional to the concentration of the species. The calculation of concentration is governed by ...
What is the wavelength of a UV spectrophotometer?
Ultraviolet visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometers use a light source to illuminate a sample with light across the UV to the visible wavelength range (typically 190 to 900 nm). The instruments then measure the light absorbed, transmitted, or reflected by the sample at each wavelength. Some spectrophotometers have an extended wavelength range, into the near-infrared (NIR) (800 to 3200 nm).
What light source is used for UV spectroscopy?
Unfortunately, such a source does not exist. Two different light sources have historically been used in UV-visible spectrophotometers: – The deuterium arc lamp was used to provide a good intensity continuum in the UV region and useful intensity in the visible region – The tungsten-halogen lamp yielded good intensity over the entire visible range and part of the UV spectrum More recently, a single Xenon flash lamp has been used more widely. The use of a Xenon flash lamp as a single source has significant advantages over the use of the two conventional lamps. Deuterium (D
How does a monochromator work?
To narrow the light down to a selected wavelength band, the light is passed through a monochromator. A monochromator consists of: – An entrance slit, – A dispersion device, to spread the light into different wavelengths (like a rainbow) and allow the selection of a nominated band of wavelengths, and – An exit slit where the light of the nominated wavelengths passes through and onto the sample. An easy way to think about a monochromator is to think of a room, with the sun shining through a window. The sunlight hits a prism that separates the white light into a rainbow. The rainbow falls onto a window on the opposite side of the room. As the prism is turned, light of different colors i.e. different wavelengths, pass out of the room through the window. Ideally, the output from a monochromator is light of a single wavelength. In practice, however, the output is always a band of wavelengths. Most spectrophotometers on the market today contain holographic gratings as the dispersion device. These optical components are made from glass, onto which extremely narrow grooves are precisely etched onto the surface. The dimensions of the grooves are of the same order as the wavelength of light to be dispersed. Finally, an aluminum coating is applied to create a reflective surface. Interference and diffraction of the light falling on the grating is reflected at different angles, depending on the wavelength. Holographic gratings yield a linear angular dispersion with wavelength and are temperature insensitive. However, they reflect light in different orders, which overlap (see Figure 12). As a result, filters must be used to ensure that only the light from the desired reflection order reaches the detector. A concave grating disperses and focuses light simultaneously.
What is a single monochromator spectrophotometer?
A single monochromator spectrophotometer is used for general-purpose spectroscopy and can be integrated into a compact optical system. Figure 13 shows a schematic diagram of a single monochromator optical system. A single monochromator spectrophotometer cannot select the wavelengths of light as narrowly as a double monochromator system, but this ability may not be required for many applications, for example when measuring samples that have broad absorption peaks.
How to determine the wavelength of electromagnetic radiation?
Because radiation acts as a wave, it can be classified in terms of either waveleng th or frequency, which are related by the following equation: ν = c/λ where ν is frequency (in seconds), c is the speed of light (3 × 108ms-1), and λ is wavelength (in meters). In UV-Vis spectroscopy, wavelength is usually expressed in nanometers (1 nm = 10-9m). It follows from the equations that radiation with shorter wavelength has higher energy, and, for UV-Vis spectroscopy, the low (short)
When light passes through or is reflected from a sample, the amount of light absorbed is the difference between the?
When light passes through or is reflected from a sample, the amount of light absorbed is the difference between the incident radiation (I
What is a tungsten halogen lamp?
Tungsten-halogen lamp The tungsten-halogen lamp uses a filament. When a current is passed through the filament, it becomes heated and emits light (see Figure 10). The lamp yields good intensity over part of the UV spectrum and over the entire visible and NIR range (350 nm- 3000 nm). This type of lamp has very low noise and low drift and typically has a functional life of 10,000 h.

What Is Uv-Vis Spectroscopy?
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy is a quantitative and analytical technique that measures the amount of visible or UV light a chemical substance absorbs through a Uv-Vis spectrometer. The technique is done by measuring light’s intensity in wavelengths that passes through a particular sample and then comparing it with a blank or a reference sample. Generally, Uv...
How Does Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Work?
- To give you a better understanding of how Uv-Vis spectroscopy works, let’s talk about its main components and the processes of how light is absorbed and measured by the spectrometer.
The Purpose and Applications of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy has been widely used in various sample testing today. This technique has the following famous innovative applications:
Advantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The best advantage of utilizing Uv-Vis spectrometers is their optimal accuracy. These machines are guaranteed to give you accurate readings, which are essential when you need to prepare chemical solutions or record the movement of the celestial bodies. Uv-Vis spectroscopy is also easy to understand with its simple analysis ability. The spectrometers are convenient and easy t…
Disadvantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The main disadvantage of Uv-Vis spectrometers is their challenging assembly, and it may take time to prepare using them. Ensure that the area where you’ll place the device is clear of any electronic noise, outside light, and other contaminants that could affect the measurements and readings of the spectrometer. A Uv-Vis spectrometer is sensitive to external factors, so you mus…
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Limitations
- Even an advanced technique like Uv-Vis spectroscopy has limitations, too. You can grasp what these are below:
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Is The Future
- UV-vis spectroscopy provides researchers and scientists with more efficient methods to measure light wavelengths, providing accurate readings that are helpful in various biological and chemical analyses. The UV-vis spectrometer device is precise and easy to operate, provided that you maintain a clean working area free from any external noise and dust that can affect the machine’…