
What is UV-Vis short for?
Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectrophotometry is a technique used to measure light absorbance across the ultraviolet and visible ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What does UV-Vis spectroscopy tell you?
UV-Vis Spectroscopy (or Spectrophotometry) is a quantitative technique used to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light. This is done by measuring the intensity of light that passes through a sample with respect to the intensity of light through a reference sample or blank.
What is the difference between UV and UV-Vis?
Key Difference – UV vs Visible Spectrophotometer There is no difference between UV and visible spectrophotometer because both these names are used for the same analytical instrument. This instrument is commonly known as the UV-visible spectrophotometer or Ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer.
Why is it called UV-Vis spectroscopy?
UV spectroscopy or UV–visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in part of the ultraviolet and the full, adjacent visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
How do you read UV-Vis?
1) Step 1: Identify the number of peaks appearing in the UV-VIS spectrum. Figure 5 shows several peaks indicating the presence of an excited electron. The easier the electrons are excited, the greater the wavelength that is absorbed, the more electrons are excited, the higher the absorbance.
How do you analyze UV data?
0:038:04UV-Vis Tutorial | Part 3: Data Analysis - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHi there welcome to part 3 in our demonstrational uv-vis video series in this installment I'llMoreHi there welcome to part 3 in our demonstrational uv-vis video series in this installment I'll discuss how to analyze your measurement data so you can calculate absorbance. And mass concentration. I'
What is the range of UV visible radiation?
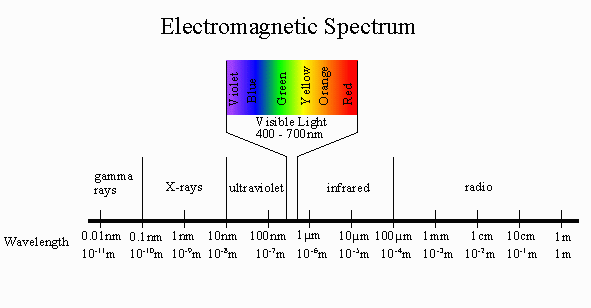
Ultraviolet–visible (UV/Vis) spectroscopy is based on the absorption of the electromagnetic radiation in UV/Vis region, with the wavelength ranges of 200–400 nm, called 'ultraviolet spectroscopy,' and 400–800 nm, called 'visible spectroscopy.
What is the difference between UV and visible light?
Ultraviolet (UV) light has shorter wavelengths than visible light. Although UV waves are invisible to the human eye, some insects, such as bumblebees, can see them.
What important information can you gain from a UV-Vis spectrum?
UV-vis spectroscopic data can give qualitative and quantitative information of a given compound or molecule. Irrespective of whether quantitative or qualitative information is required it is important to use a reference cell to zero the instrument for the solvent the compound is in.
What is difference between IR and UV spectroscopy?
The key difference between IR and UV and visible spectroscopy is that IR spectroscopy uses the low-energy infrared part of the spectrum, whereas UV and visible spectroscopy use UV and visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What you mean by absorbance?
Absorbance (A), also known as optical density (OD), is the quantity of light absorbed by a solution. Transmittance is the quantity of light that passes through a solution.
What is the unit of absorbance?
absorbance units (Au)Absorbance is measured in absorbance units (Au), which relate to transmittance as seen in figure 1. For example, ~1.0Au is equal to 10% transmittance, ~2.0Au is equal to 1% transmittance, and so on in a logarithmic trend.
How can UV-Vis spectroscopy be used to determine the concentration of a substance?
This article more specifically explores techniques when using a spectrophotometer to determine concentration of an analyte. A UV/VIS spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light passing through a sample solution in a cuvette, and compares it to the intensity of the light before it passes through the sample.
Why most absorption bands in the visible UV spectrum are very broad?
In UV-Visible spectra Bonds will be in constant vibration, this variation will absorb nearby energies i.e, ΔE , for this reason UV peaks are broader.
What is the difference between UV-Vis spectroscopy and IR spectroscopy?
The key difference between IR and UV and visible spectroscopy is that IR spectroscopy uses the low-energy infrared part of the spectrum, whereas UV and visible spectroscopy use UV and visible regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Which molecule absorbs at the longer wavelength?
Molecule ASolution. Molecule A has a longer system of conjugated pi bonds, and thus will absorb at a longer wavelength.
Why is UV spectroscopy used in pharmaceutical analysis?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, abou...
What are the applications of spectrophotometry?
In different fields, such as astronomy, molecular biology , chemistry and biochemistry, spectrophotometers are commonly used. Specification applica...
What is the range of UV spectroscopy?
UV-Vis is also considered a general procedure, since in the UV-visible wavelength spectrum, most molecules absorb light. The UV frequency is betwee...
Which lamp is used in UV spectroscopy?
Light with a wavelength range between 190 nm and 800 nm is radiated through the cuvette using a spectrometer and absorption spectrums are recorded....
What is the IR principle?
The principle of IR spectroscopy utilises the idea that molecules appear to absorb unique light frequencies that are typical of the molecules’ corr...
What is UV VIS spectroscopy and how does it work?
UV-Vis is a quick , convenient, and inexpensive way of determining the solution concentration of an analyte. In UV-Vis, a beam travels through a so...
What is UV Vis?
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte. Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV / Vis) in the ultraviolet-visible spectral field refers to absorption spectroscopy ...
What is UV VIS Spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-VIS) Spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the analyte quantity depending on the amount of light received by the analyte.
What is UV spectrophotometer?
UV spectrophotometers measure the visible regions of ultraviolet light and can provide valuable information, as well as detect any impurities, about the levels of active ingredients present in pharmaceutical compounds.
What is the wavelength of UV spectroscopy?
The UV frequency is between 100 and 400 nm, and the visible spectrum is between 400 and 700 nm.
Where are UV visible spectrophotometers used?
UV-Visible Mid-range to Upper-end Spectrophotometers are typically used in research laboratories, including university and industrial laboratories.
Where does UV radiation come from?
Radiation is transmitted deep into the UV zone through the quartz envelope. The most popular source is the deuterium lamp for the UV region itself, and a UV-Visible spectrometer would normally have all types of lamps to fill the whole wavelength spectrum.
Is UV spectral band accurate?
Generally, the UV and visible spectral bands of substances are large. And may not exhibit a high degree of compound recognition accuracy. Nonetheless, they are sufficient for quantitative assays and are useful as an alternate means of detection for several substances. The radiation from typical hot solids consists of several wavelengths and depends primarily on the temperature of the solid and is predictable from the principle of chance, the energy released at each given wavelength.
What is UV spectroscopy?
UV Vis spectroscopy is a type of absorption spectroscopy in which a sample is illuminated with electromagnetic rays of various wavelengths in the ultraviolet (UV) and visible (Vis) ranges. Depending on the substance, the UV or visible light rays are partially absorbed by the sample. The remaining light, i.e. the transmitted light, is recorded as a function of wavelength by a suitable detector. The detector then produces the sample's unique UV Vis spectrum (also known as the absorption spectrum).
How to analyze a compound with UV spectroscopy?
Molecules can be analyzed using UV Vis spectroscopy if they possess any functional group or conjugation, or if they produce a color complex. As inorganic compounds do not contain any functional group or conjugation, the common method for analyzing them is by reaction with a suitable compound. This produces a color complex whose absorbance can be photometrically measured in the visible region and correlated with its actual concentration. For example, iron is commonly analyzed by a reaction with 1, 10-phenthroline to produce a red color complex. The absorbance of the complex is measured at 570 nm to estimate iron concentration.
Why is the sample compartment open in UV spectrophotometers?
The sample compartment in UV Vis array spectrophotometers is open due to the fact that array instruments use reverse optics and the simultaneous detection of all wavelengths of the spectrum.
What happens to the absorption of UV light?
The absorption of UV light results in electronic transitions from lower energy levels to higher energy levels. Absorption of ultraviolet radiation in organic molecules is restricted to certain functional groups (chromophores) that contain valence electrons of low excitation energy. The molecular transitions/interactions that take place due to UV absorption are:
What is UV VIS?
UV–vis is a commonly used technique to characterize nanoparticles. This technique allows to confirm the nanoparticles formation by measuring the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). This procedure can provide information about the size, stability, and aggregation of the NPs [4].
What is UV visible spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet (UV)-visible spectroscopy is a type of absorption spectroscopy in which UV-visible light is absorbed by the molecule. Absorption of the UV-visible radiations results in the excitation of the electrons from lower to higher energy levels. In organic molecules only certain functional groups (chromophores) that contain valence electrons of low excitation energy can absorb ultraviolet and visible radiation. C-Cyts represent an ideal target molecule for UV-visible spectroscopy because of the large absorption of heme groups. The strong UV-visible absorption bands of the heme originate from the π→π* transitions, providing information about the type of heme, the oxidation, and the spin state of the central iron ion. UV-visible spectroscopy allows in vivo measurements of biofilms under physiologically relevant conditions (Fig. 4D ). In order to detect all the cytochromes (OMCs and inner membrane cytochromes) along the biofilm thickness without any spatial distinction growing the EABs on a transparent electrode (indium tin oxide) is suggested. 78 Moreover, by combining different experimental set-ups is possible to obtain a UV-visible spectrum of the OMCs only confined in the proximity of the electrode surface.
What is FUV spectroscopy used for?
Moreover, FUV spectroscopy can be utilized for qualitative and quantitative analyses of various liquid and solid samples, because each molecule shows a characteristic FUV spectrum with strong absorption, and intensities and wavelengths of FUV bands are very sensitive to changes in concentration, temperature, pH, and so on [ 46–50].
What are the advantages of FUV spectroscopy?
The most fundamental advantage of FUV spectroscopy is that it contains unique information about the electronic transitions and structure of molecules. One can obtain knowledge about them that is not accessible by any other spectroscopy.
Why are C-cyts used in UV spectroscopy?
C-Cyts represent an ideal target molecule for UV-visible spectroscopy because of the large absorption of heme groups. The strong UV-visible absorption bands of the heme originate from the π→π* transitions, providing information about the type of heme, the oxidation, and the spin state of the central iron ion.
Is UV spectroscopy useful for metathesis?
UV/visible spectroscopy is useful for the monitoring of organometallic species , but is not useful for monitoring the organic component of typical metathesis reactions. Ruthenium species relevant to alkene metathesis are typically very highly colored (red or green) and have molar absorptivities of c.103L mol−1cm−1.54,55This technique has therefore been heavily used for the study of precatalyst initiation, where the decrease in the absorbance for the precatalyst can be monitored over time and used to obtain rate constants for precatalyst initiation with different complexes, substrates, or in different solvents.
What Is Uv-Vis Spectroscopy?
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy is a quantitative and analytical technique that measures the amount of visible or UV light a chemical substance absorbs through a Uv-Vis spectrometer. The technique is done by measuring light’s intensity in wavelengths that passes through a particular sample and then comparing it with a blank or a reference sample. Generally, Uv...
How Does Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Work?
- To give you a better understanding of how Uv-Vis spectroscopy works, let’s talk about its main components and the processes of how light is absorbed and measured by the spectrometer.
The Purpose and Applications of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- Uv-Vis Spectroscopy has been widely used in various sample testing today. This technique has the following famous innovative applications:
Advantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The best advantage of utilizing Uv-Vis spectrometers is their optimal accuracy. These machines are guaranteed to give you accurate readings, which are essential when you need to prepare chemical solutions or record the movement of the celestial bodies. Uv-Vis spectroscopy is also easy to understand with its simple analysis ability. The spectrometers are convenient and easy t…
Disadvantages of Uv-Vis Spectroscopy
- The main disadvantage of Uv-Vis spectrometers is their challenging assembly, and it may take time to prepare using them. Ensure that the area where you’ll place the device is clear of any electronic noise, outside light, and other contaminants that could affect the measurements and readings of the spectrometer. A Uv-Vis spectrometer is sensitive to external factors, so you mus…
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Limitations
- Even an advanced technique like Uv-Vis spectroscopy has limitations, too. You can grasp what these are below:
Uv-Vis Spectroscopy Is The Future
- UV-vis spectroscopy provides researchers and scientists with more efficient methods to measure light wavelengths, providing accurate readings that are helpful in various biological and chemical analyses. The UV-vis spectrometer device is precise and easy to operate, provided that you maintain a clean working area free from any external noise and dust that can affect the machine’…