What is a 9g work visa in the Philippines?
Work Visas: 9 (g) Pre-Arranged Employee Commercial Visa The 9 (g) or Pre-Arranged Employee Visa Commercial is the most common type of work visa availed by foreign nationals engaged in gainful employment in the Philippines.
What is the PWP for 9g visa?
The PWP is a document, which authorizes the foreigner to start working even while the AEP or 9g visa is still in process. It can be filed as soon as the AEP application is filed and can be obtained after 2 weeks. We can facilitate your 9g visa non-commercial application, inclusive of the services below:
What are the documents required for a 9g working visa?
The following documents are required for the application of a 9G working visa: Notarized document from your local or locally-based employer; Alien Employment Permit from the Department of Labor and Employment; Clearance certificate from the Bureau of Immigration; Applicant’s passport.
Can a 9g commercial visa holder downgrade to a 9a visitor visa?
Additionally, holders of 9g commercial visa who are promoted to a higher position in the same company are exempted by the Bureau of Immigration from downgrading to a 9a visitor visa and applying for another 9g visa, pursuant to Board Resolution No. EED-15-01. This resolution is only effective provided that foreign nationals:

How can I get 9G visa in Philippines?
9G Visa Requirements: Latest ITR of the Petitioner. SEC registration, incorporation papers, and GIS of the Petitioner, or DTI and Mayor's Permit in case of a Sole Proprietorship business. Alien Employment Permit (AEP) Notarized certification of the number of foreign and Filipino employees from the petitioning company.
How long is 9G visa in Philippines?
You may have an initial period of one (1), two (2) or three years (3) validity on your 9(g) Pre-Arranged Employees – Commercial visa. You may also extend said visa for one (1), two (2) or three year (3) years depending on the Employer-Employee Contract.
How much does a 9G visa cost?
Conversion to Pre-Arranged Employee - CommercialVALIDITYPRINCIPAL1 YearPhp 10,630.002 YearsPhp 18,170.003 YearsPhp 25,710.00Additional Fee for ACR I-Card 1 Year - + US $50 2 Years - + US $100 3 Years - + US $150 *Fees are updated as of 06 March 2014 and may change without prior notice.
How long does a 9G visa take to process?
3-4 weeksProcessing time: 3-4 weeks. The 9(g) visa application should be made to the Bureau of Immigration, within fifteen days of the issuance of the Alien Employment Permit (AEP). Fingerprints and a biometric photograph will be taken. A company representative must also attend the interview.
Is 9G visa multiple entry?
This is the most common multi-entry working visa applied by companies to their expats. A 9G visa allows their expats to work for 1, 2, or 3 years; depending on the duration of his employment, while elected company officials are allowed 1-year 9G visa.
How can I get permanent visa in Philippines?
To qualify for this visa, the applicant must prove that: He contracted a valid marriage with a Philippine citizen. The marriage is recognized as valid under existing Philippine laws. There is no record of any derogatory information against him in any local or foreign law enforcement agency.
How can a foreigner stay longer in the Philippines?
Foreign nationals can enjoy longer visa extension (six months) under a single transaction. The visa costs Php 13,900 for visa-required nationals and Php 11,500 for non-visa required nationals. Foreign travelers can prolong their stay in PH without the need to frequently visit BI for processing of documents.
Can you go to jail for overstaying your visa?
“[U]under current law, illegal entry into the United States makes an alien subject to a Federal criminal misdemeanor with a maximum penalty of 6 months in prison. However, unlawful presence itself, such as by overstaying a visa, is not a criminal offense, but only a civil ground of inadmissibility…
How much is the penalty for overstaying in the Philippines?
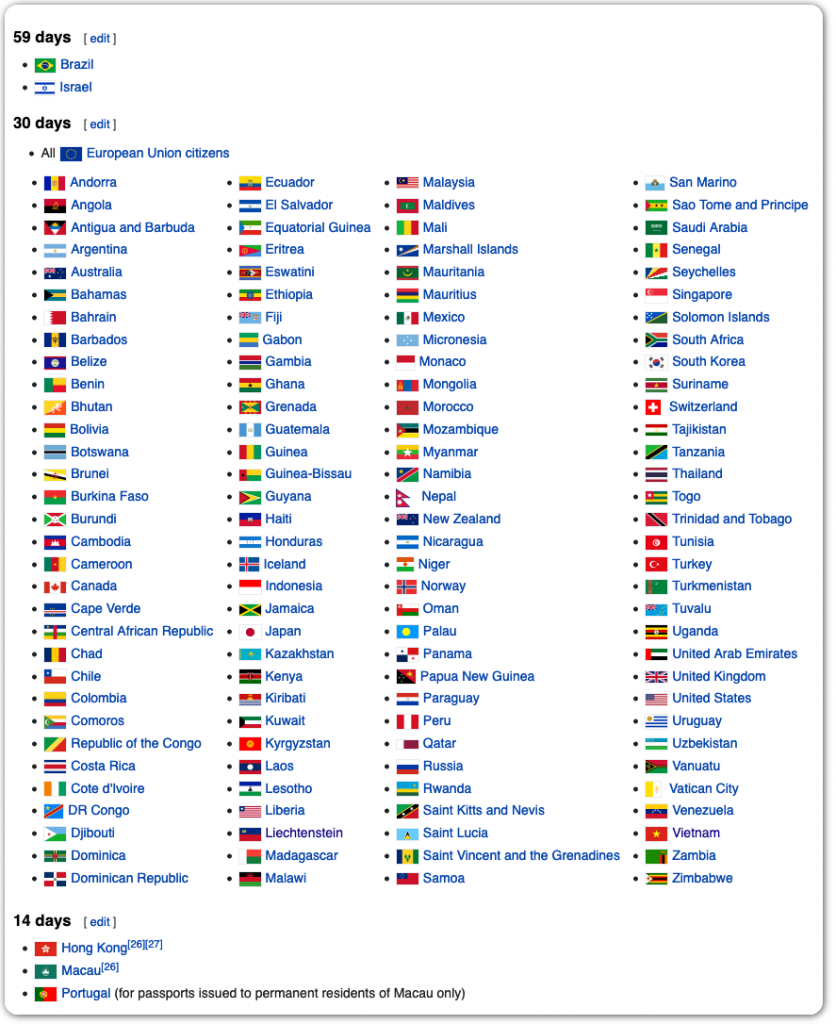
Php 500.00 per monthFine for Overstaying – (additional) Php 500.00 per month. Motion for Reconsideration for Overstaying – (additional) Php 500.00 + Php 10.00 (LRF)...Extension of Authorized stay Beyond 59 days.ITEM DESCRIPTIONMINOR Below 14 years old1 month2 monthEvery month of extensionPhp 500. 00Php 1, 000. 00Application fee300. 00300. 009 more rows
How long after visa interview will I get my visa?
If you are found eligible to receive a visa on the day of the interview you should allow approximately 10-15 working days for your application to be processed. Your documents will be returned to you in a large envelope.
How much is the visa fee for Philippines?
The visa for the Philippines costs around $37 USD. Depending on how you obtain the visa as a foreign citizen, you may incur processing fees that can range from $20 USD to $60 USD. Other fees may also apply.
How do I know if my visa is approved?
Check the Status of a Visa Application For nonimmigrant visas, call 1-603-334-0888. Or use the Consular Electronic Application Center (CEAC).
How much is working visa in the Philippines?
PROVISIONAL WORK PERMITApplication Fee2,000.00Legal Research Fee20.00Express Lane Fee (Certification)500.00Express Lane Fee (Filing)500.00Total4,040.004 more rows
How much is the visa fee for Philippines?
The visa for the Philippines costs around $37 USD. Depending on how you obtain the visa as a foreign citizen, you may incur processing fees that can range from $20 USD to $60 USD. Other fees may also apply.
What are the types of visa in the Philippines?
Travelers who go to the Philippines as foreign citizens can get one of the following types of visas to legally enter the country: Tourism, Electronic Travel Authorization, Non-Immigrant, Quota Immigrant, Service, and Long-Term visas for leisure, tourism, and extended stays longer than 90 days.
How much does working visa cost?
The application fee for the most common nonimmigrant visa types is $160. This includes tourist, business, student, and exchange visas. Most petition-based visas, such as work and religious visas, are $190.00.
Pre-Arranged Employees (Commercial) Visa (9G)
Any foreign national wishing to work in the Philippines must obtain a valid work visa, normally the 9 (G) visa.
A 1 year 9G Visa will cost
Php 10,630 for the Principal Applicant Php 8,620 for the Dependent Spouse Php 8,370 for the Dependent Child B16 Php 7,870 for the Dependent Child B14
How many visas are there in the Philippines?
The Philippine Immigration Act prescribes fourteen different visas grouped into two main categories:
How long do you need a visa to visit the Philippines?
These are some of the differences between the various visas to consider when thinking about visiting or moving to the Philippines: A tourist visa is only necessary for stays exceeding 30 days and depending on the traveler’s country of citizenship.
What is a Section 13 visa?
Section 13 visas (immigrant visas), for foreign nationals who wish to become permanent residents in the Philippines
How many quotas are granted per year?
A maximum of 50 quota immigrant visas are granted per year
What documents are needed to move to the Philippines?
Those considering moving to the Philippines with their family should note that other requirements for an immigrant visa include their children’s birth certificates and a marriage certificate . These documents must be notarized.
How long do you have to stay in the Philippines to get a visa?
A great number of nationalities are not required to obtain a visa if they’re staying for no longer than 30 days.
What is a non-immigrant visa?
A non-immigrant visa is granted for the purpose of pre-arranged employment, trade, transit, and education. The requirements vary